Industry Overview
As we progress through 2025, Australia’s mining sector remains a pivotal contributor to the national economy, accounting for approximately 15% of the country’s GDP and providing employment to over 1.1 million individuals. This includes 300,000 jobs within the Mining Equipment, Technology, and Services (METS) sector. Despite its significance, the industry faces a multifaceted landscape shaped by economic fluctuations, environmental considerations, and technological advancements.
Commodity Market Trends
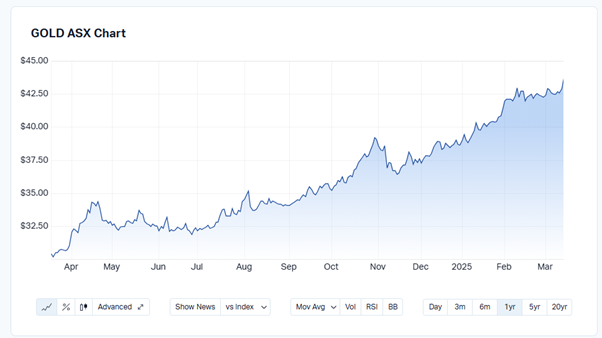
Copper and Gold: Influencing Workforce Dynamics
The prices of copper and gold are anticipated to be primary drivers of employment trends in the hard rock mining sector. An uptick in exploration activities is expected, particularly on Australia’s West Coast, although securing financing may pose challenges for some mining operations.
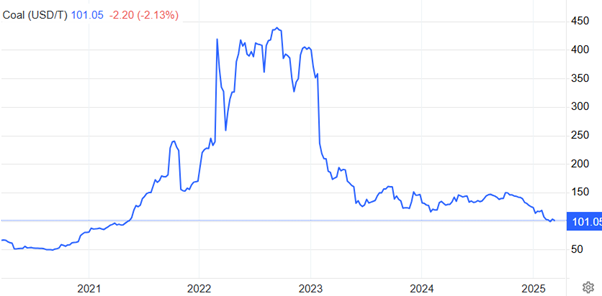
Iron Ore and Coal: Adapting to Global Shifts
Market consensus suggests that iron ore prices will remain subdued through to 2026, influenced by new supply channels and a decline in steel demand from China. Similarly, the long-term outlook for metallurgical coal exports is declining, with international demand diminishing. These trends necessitate strategic adaptations within Australia’s mining industry to maintain competitiveness.

Environmental and Sustainability Initiatives
Decarbonisation Efforts
The global emphasis on decarbonisation, which gained momentum in 2015, continues to influence the mining sector. Australian mining companies are actively pursuing strategies to reduce carbon emissions, aligning with international sustainability goals and enhancing their social license to operate.
We are seeing many mining operators align their company goals and strategies around harnessing fleets and new technologies that reduce or eliminate carbon emissions. This is through a variety of methods including electrification, clean energy, carbon capture and storage, improved efficiency.

Government Policies and Critical Minerals
Governments are increasing investments in critical minerals essential for the green transition. For instance, the U.S. administration has introduced tax credits for mining and extraction costs of critical minerals, a move that could impact global markets and present opportunities for Australian producers.
Technological Advancements and Digitalisation
Automation and Electrification
The integration of automation and electrification technologies is transforming mining operations, leading to increased efficiency and reduced environmental footprints. Australian mining companies are at the forefront of adopting these innovations, setting benchmarks for global industry standards.
The Australian mining industry is the second largest contributor to carbon emissions (102 Mt CO2 -e pa) so it makes sense that reducing emissions is becoming a key focus. When we break that down even more the diesel-powered haul truck fleets are responsible for up to 80% of a mine’s emissions. The continued adoption of electric haul trucks fleets will provide the fastest gain to the push to reduce emissions.

Data-Driven Maintenance
The application of big data and advanced analytics is becoming crucial for predictive maintenance. By leveraging these technologies, maintenance leaders can anticipate equipment failures and optimise maintenance schedules, thereby minimising downtime and reducing costs.
Workforce Challenges
Skills Shortages
The mining industry continues to grapple with a significant shortage of skilled labour. Enrolment in mining engineering programs has declined, and attracting new talent remains a challenge. Maintenance leaders must focus on upskilling current employees and implementing training programs that address the evolving technological landscape.
Safety and Productivity
Enhancing worker safety while maintaining productivity is a critical balance. Investments in safety training and the adoption of safer, more efficient equipment are essential. Maintenance leaders play a pivotal role in ensuring that safety protocols are rigorously followed while optimising operational efficiency.
Capital and Cost Management
Rising Costs
The cost of labour, materials, and technology has been on the rise, partly due to lingering impacts from the COVID-19 pandemic. Maintenance leaders must develop strategies to manage these costs effectively while maintaining the reliability and efficiency of mining operations.
Investment in Innovation
Despite capital constraints, investing in innovative technologies and processes is crucial for long-term success. Maintenance leaders need to make a compelling case for these investments by demonstrating their potential to enhance productivity and reduce costs over time.
A good example of the push for innovation can be seen at this year’s Global Resources Innovation Expo in Brisbane May 20-22, 2025. At this show there will be an Innovation Zone which as the site says is, “empowering the future of innovation”.

Conclusion
The Australian mining industry in 2025 presents a complex array of challenges and opportunities for maintenance leaders. By embracing technological advancements, addressing workforce challenges, adhering to new environmental regulations, and managing costs effectively, maintenance leaders can navigate these pressures successfully and contribute to the sustainable growth of the industry.
For more detailed insights and updates, you can refer to sources such as Deloitte’s “Tracking the Trends 2025” report, the Department of Industry, Science, and Resources’ quarterly reports, and various industry analyses from platforms like Australian Mining and METS Insight.